Compact, efficient, reliable and safe – BorgWarner’s newest traction inverter ticks all the boxes for smooth integration in the next generation of electric vehicles
Each new generation of electric vehicles strives to satisfy customer expectations of greater driving range and easier affordability. For vehicle designers, this translates to the need for lighter and more compact drivetrains with higher electrical and mechanical efficiencies, while constraining costs without compromising safety. In preparation, BorgWarner has updated its inverter technology with a redesigned power module, cooling module and electrical control system, plus streamlined production techniques to improve efficiency, reliability and ease of integration.
The next generation inverter is an 800VDC system with power ratings scalable up to 400kVA to suit the requirements of passenger and medium power commercial vehicles. It also meets the US Department of Energy (DOE) Vehicle Technologies Office (VTO) 2025 target of 10kW/liter power density at a cost of USD2.7/kW or less.

Compact
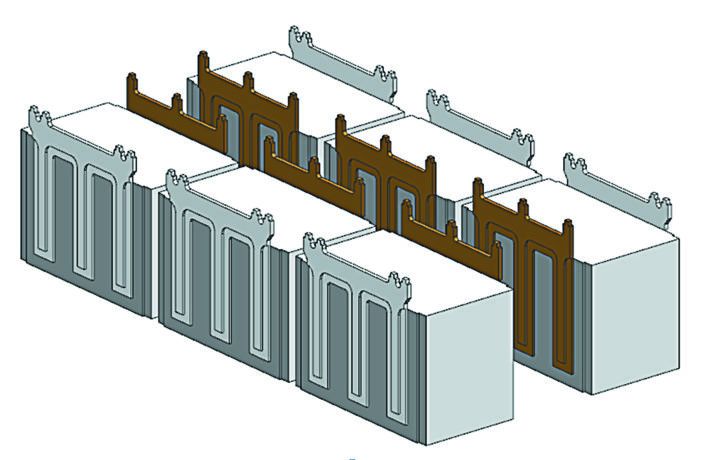
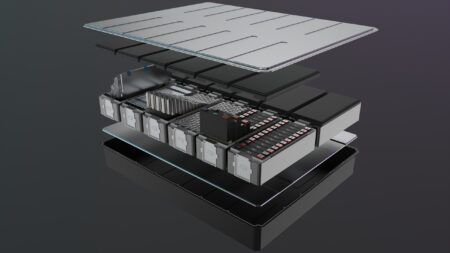
System characteristics including operating voltage, peak phase current, voltage ripple, switching frequencies and slew rates govern the physical size of the largest inverter component – the bulk capacitor. By using next generation capacitors segmented into smaller blocks (Figure 1) this has been minimized to achieve scalability, increase power density and improve thermal performance. A combination of assembly process improvements and higher component integration gives the inverter an active component volume of less than four liters and a dry weight of around 7kg (Figure 2).

Efficient and Reliable
BorgWarner’s Viper power module is used in a single switch design with dual-sided cooling, keeping the same footprint for each power class. The type/number of silicon carbide (SiC) dies and the cooling module configuration can be adjusted for a perfect match to a customer’s application. The power module can operate reliably at junction temperatures beyond the typical 175°C, while boosting efficiency by reducing system losses and carrying additional current with a similar or lower SiC active material area compared to previous designs.
The cooling module matches thermal management to each power device in the package. The cost-effective design employs heatsink components – base, novel cooling fin structure and cover – stamped from high thermal conductivity copper alloy and brazed together (Figure 3). To further improve reliability, the dual sided cooling architecture allows the use of different thermal interface materials and a variety of joining methods on the top and bottom of the power module.

Safe
Inverter safety is of paramount importance – this is a high voltage machine delivering peak RMS phase currents of up to 650A, and commanding considerable accelerative forces. BorgWarner’s next generation inverter attains Automotive Safety Integrity Level (ASIL) D, the highest rank in the ISO 26262 standard. The electrical control architecture was redesigned to include the company’s new Inverter System Safety ASIC (INSSA) to help achieve this target (Figure 4).
Each INSSA helps to provide a fully independent power supply to the gate drivers; a single point electrical fault in the inverter causes the system to maintain a safe operational state independently of microprocessor intervention. This ability to monitor and react to system diagnostic data to keep the high voltage bus within a safe range is a key advantage of BorgWarner’s new technology. A highly reliable feedback loop for sensing, control and actuation allow the controller and gate driver circuitry to share the single main board, reducing the layout footprint.
Summary
BorgWarner design innovation has delivered a compact, efficient, reliable and safe next generation traction inverter with industry-leading, fault-tolerant control architecture.